Professional guidance
Optimizing Investments: Rental Property Market Analysis Essentials

Optimizing Investments: Rental Property Market Analysis Essentials
Investing in rental properties requires a strategic approach that goes beyond purchasing a property. Conducting a comprehensive market analysis is a key step in optimizing your investments and ensuring long-term success. In this article, we’ll explore the essential elements of rental property market analysis and how it can contribute to making informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Local Real Estate Landscape
Before diving into the specifics of a particular property, it’s crucial to understand the broader local real estate landscape. Analyze trends in property values, rental rates, and vacancy rates in the area. A thorough understanding of the local market sets the foundation for making informed decisions about potential investments.
Assessing Rental Demand and Supply
A critical aspect of rental property market analysis is assessing the demand and supply dynamics. Evaluate the current demand for rental properties in the area and compare it with the available supply. A high demand and limited supply often indicate a favorable market for landlords, providing opportunities for competitive rental rates and occupancy.
Analyzing Economic Indicators
Consider economic indicators that may impact the rental market. Factors such as job growth, population trends, and overall economic stability can influence the demand for rental properties. Analyzing these indicators helps in predicting the potential for sustained rental income and property appreciation over time.
Evaluating Neighborhood Desirability
The desirability of the neighborhood plays a significant role in the success of a rental property. Consider factors such as proximity to amenities, safety, school quality, and public transportation. Understanding the neighborhood’s appeal helps in targeting tenants looking for a specific lifestyle, ultimately affecting the property’s marketability.
Reviewing Historical Rental Performance
Examine the historical performance of rental properties in the area. This includes rental appreciation rates, average vacancy durations, and overall return on investment. Historical data provides insights into the stability and profitability of the rental market, guiding your investment decisions based on past performance trends.
Estimating Potential Rental Income
One of the primary goals of rental property market analysis is to estimate potential rental income accurately. Consider factors such as comparable rental rates, property size, and amenities to determine a competitive yet profitable rental price. Accurate income estimates are crucial for financial planning and investment viability.
Accounting for Operating Expenses
While rental income is essential, it’s equally crucial to account for operating expenses. Consider property taxes, maintenance costs, property management fees, and any other recurring expenses. A thorough understanding of these costs ensures that your expected returns align with the overall financial health of the investment.
Projecting Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculate the projected return on investment by factoring in both rental income and operating expenses. A positive ROI indicates a financially sound investment. This projection helps investors compare different properties and make decisions based on the potential for long-term profitability.
Staying Informed About Legal and Regulatory Factors
Rental property market analysis should also consider legal and regulatory factors that may impact the investment. Stay informed about local landlord-tenant laws, zoning regulations, and any upcoming
Navigating Lease Renewal: Important Considerations

Exploring Important Considerations in Lease Renewal
Lease renewal is a crucial phase for both landlords and tenants. Navigating this process successfully involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure a positive outcome for all parties involved. This guide provides insights into key considerations during lease renewal.
1. Reviewing the Current Lease Agreement
Before initiating the lease renewal process, both landlords and tenants should thoroughly review the current lease agreement. Understanding the existing terms, conditions, and any changes made during the previous lease period lays the groundwork for a smooth renewal process.
2. Communication and Early Planning
Clear communication is vital during lease renewal. Initiating discussions well in advance provides ample time for both parties to express their preferences and negotiate terms. Early planning reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings and allows for a collaborative approach to the renewal process.
3. Evaluating Rent and Lease Terms
One of the primary considerations during lease renewal is the evaluation of rent and lease terms. Landlords may assess market conditions to determine whether rent adjustments are necessary, while tenants may negotiate for favorable lease terms. Finding a balance that suits both parties contributes to a successful renewal.
4. Assessing Property Conditions
Landlords should conduct a thorough assessment of the property’s condition before offering a lease renewal. This includes addressing any necessary repairs or maintenance issues. On the tenant’s side, ensuring that the property remains in good condition according to the lease agreement is crucial for a positive renewal outcome.
5. Understanding Local Regulations
Lease renewal considerations also extend to understanding local regulations governing the process. Different jurisdictions may have specific rules regarding notice periods, rent increases, and other aspects of lease renewals. Adhering to these regulations is essential to avoid legal complications.
6. Offering Incentives for Renewal
To encourage tenants to renew their leases, landlords may consider offering incentives. This could include a modest rent discount, an upgrade in amenities, or other perks that add value to the tenant’s living experience. Incentives can foster positive tenant-landlord relationships and increase the likelihood of renewal.
7. Exploring Alternatives and Flexibility
Both landlords and tenants should approach lease renewal with a degree of flexibility. Exploring alternative lease terms, such as a shorter or longer lease duration, and being open to negotiations can lead to a mutually beneficial agreement. Flexibility enhances the chances of reaching a consensus.
8. Clarifying Renewal and Notice Procedures
Clearly outlining renewal procedures and notice requirements is crucial for a smooth lease renewal process. Both parties should be aware of the steps involved, including providing proper notice and adhering to any specific procedures outlined in the lease agreement or local regulations.
9. Considering Tenant Satisfaction
For landlords, considering tenant satisfaction is key to successful lease renewals. Addressing tenant concerns, maintaining open communication, and demonstrating responsiveness contribute to positive tenant experiences. Satisfied tenants are more likely to renew their leases and may even recommend the property to others.
10. Seeking Professional Guidance
In complex lease renewal scenarios or when legal matters arise, seeking professional guidance is
Navigating the Eviction Process: Rights and Responsibilities
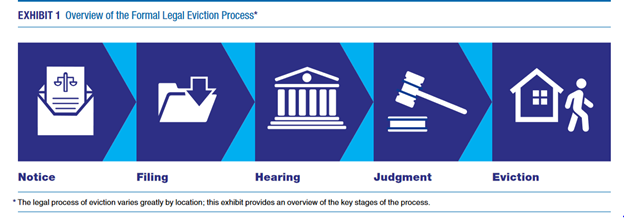
Understanding the Eviction Process: Rights and Responsibilities
The eviction process is a legal procedure that landlords may initiate to regain possession of their property. For tenants, understanding their rights and responsibilities during this challenging situation is crucial. This article delves into the eviction process, offering insights into the steps involved, legal considerations, and the rights of both landlords and tenants.
Initiating the Eviction: A Last Resort for Landlords
Evictions typically arise when a tenant fails to meet their lease obligations, such as non-payment of rent or violating terms outlined in the lease agreement. Landlords often view eviction as a last resort after attempts to resolve issues through communication or alternative solutions have proven unsuccessful. It is a legal process that must adhere to specific guidelines and regulations.
Issuing the Eviction Notice: Formal Communication
The eviction process usually begins with the landlord serving an eviction notice to the tenant. This formal communication outlines the reasons for eviction and a specified period within which the tenant must remedy the situation or vacate the premises. The type of notice and the duration provided vary depending on local laws and the reason for eviction.
Tenant’s Response and Options: Understanding Legal Rights
Upon receiving an eviction notice, tenants have legal rights and options. They may choose to address the issues mentioned in the notice, such as paying overdue rent or rectifying lease violations, within the stipulated timeframe. Additionally, tenants may seek legal advice to understand their rights and explore any available defenses against eviction.
Legal Grounds for Eviction: Lease Violations and Non-payment
Evictions are typically grounded in specific lease violations or non-payment of rent. Common lease violations include unauthorized subletting, property damage, or engaging in illegal activities on the premises. Non-payment of rent is a prevalent reason for eviction, and tenants failing to meet their financial obligations may face legal consequences.
Filing an Eviction Lawsuit: Legal Procedures
If a tenant does not address the issues outlined in the eviction notice, the landlord may proceed to file an eviction lawsuit, also known as an unlawful detainer action. This legal procedure involves submitting a complaint to the court, specifying the reasons for eviction and seeking a court order to regain possession of the property.
Court Hearing and Judgment: The Legal Process Unfolds
After filing an eviction lawsuit, both parties are summoned to a court hearing. During the hearing, each party presents their case, and the judge makes a judgment based on the presented evidence and applicable laws. If the court rules in favor of the landlord, a judgment for possession is issued.
Execution of Eviction: Regaining Possession
Following a court judgment, the landlord may obtain a writ of possession, allowing law enforcement to physically remove the tenant from the property. The execution of the eviction involves coordinating with law enforcement to regain possession of the premises. This step is often considered a last resort and is carried out under the supervision of authorities.
Aftermath of Eviction: Tenant’s Responsibilities
Once evicted, tenants face several responsibilities, including removing personal
Tax Strategies for Rental Properties: Maximizing Returns and Compliance

Tax Strategies for Rental Properties: Maximizing Returns and Compliance
Investing in rental properties offers potential financial gains, but understanding the intricacies of rental property taxation is crucial for both landlords and investors. Implementing effective tax strategies not only maximizes returns but also ensures compliance with applicable tax laws.
Navigating Tax Deductions for Rental Properties
One of the key aspects of rental property taxation is understanding and leveraging available tax deductions. Landlords can typically deduct expenses such as mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, maintenance costs, and depreciation. Keeping meticulous records of these expenses is essential for accurate tax reporting.
Depreciation and its Impact on Taxes
Depreciation is a significant tax benefit for rental property owners. While the property may appreciate in value over time, the IRS allows landlords to claim depreciation as an expense. This non-cash deduction reduces taxable income, providing a valuable tax advantage for property investors.
Understanding Passive Activity Loss Rules
Passive activity loss rules come into play when rental property owners incur more expenses than income. It’s essential to comprehend these rules to navigate the tax implications effectively. Losses from rental activities may be limited, and understanding how these rules apply is crucial for tax planning.
Tax Implications of Rental Income
Rental income is subject to taxation, but the way it is taxed depends on various factors. Landlords may be taxed at their ordinary income tax rate on rental profits. However, qualifying real estate professionals or those with active involvement in property management may benefit from different tax treatment.
Utilizing 1031 Exchanges for Tax Deferral
Investors looking to defer taxes on capital gains from the sale of a rental property can explore 1031 exchanges. This provision allows for the exchange of one investment property for another without immediate tax consequences. Properly executed, a 1031 exchange can facilitate the growth of a real estate portfolio.
Tax Considerations for Short-Term Rentals
For landlords engaging in short-term rentals, tax considerations may differ. Income generated from short-term rentals is typically treated as ordinary income, and expenses can be deducted accordingly. Understanding the specific tax rules for short-term rentals is vital for accurate reporting.
State and Local Tax Variations
Tax laws can vary significantly at the state and local levels. It’s crucial for landlords to be aware of and comply with regional tax regulations related to rental properties. Consulting with tax professionals familiar with local tax codes ensures accurate reporting and compliance.
Record Keeping and Documentation
Thorough record-keeping is a fundamental aspect of effective rental property taxation. Maintaining organized records of income, expenses, and relevant documents allows landlords to substantiate deductions and comply with tax regulations. Digital tools and software can simplify the record-keeping process.
Tax Planning and Professional Guidance
Engaging in proactive tax planning is essential for rental property owners. Seeking professional guidance from tax advisors or accountants specializing in real estate can provide valuable insights. Professionals can help landlords optimize their tax positions, navigate complex regulations, and stay informed about changes in tax laws.
Staying Informed About Tax Law Changes
Tax
