Landlord rights
Navigating the Eviction Process: Rights and Responsibilities
Understanding the Eviction Process: Rights and Responsibilities
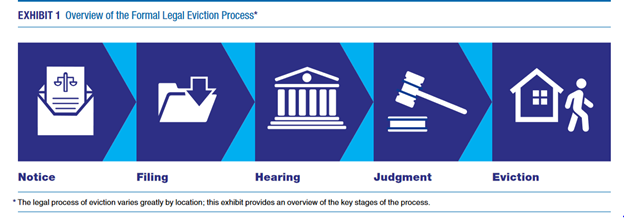
The eviction process is a legal procedure that landlords may initiate to regain possession of their property. For tenants, understanding their rights and responsibilities during this challenging situation is crucial. This article delves into the eviction process, offering insights into the steps involved, legal considerations, and the rights of both landlords and tenants.
Initiating the Eviction: A Last Resort for Landlords
Evictions typically arise when a tenant fails to meet their lease obligations, such as non-payment of rent or violating terms outlined in the lease agreement. Landlords often view eviction as a last resort after attempts to resolve issues through communication or alternative solutions have proven unsuccessful. It is a legal process that must adhere to specific guidelines and regulations.
Issuing the Eviction Notice: Formal Communication
The eviction process usually begins with the landlord serving an eviction notice to the tenant. This formal communication outlines the reasons for eviction and a specified period within which the tenant must remedy the situation or vacate the premises. The type of notice and the duration provided vary depending on local laws and the reason for eviction.
Tenant’s Response and Options: Understanding Legal Rights
Upon receiving an eviction notice, tenants have legal rights and options. They may choose to address the issues mentioned in the notice, such as paying overdue rent or rectifying lease violations, within the stipulated timeframe. Additionally, tenants may seek legal advice to understand their rights and explore any available defenses against eviction.
Legal Grounds for Eviction: Lease Violations and Non-payment
Evictions are typically grounded in specific lease violations or non-payment of rent. Common lease violations include unauthorized subletting, property damage, or engaging in illegal activities on the premises. Non-payment of rent is a prevalent reason for eviction, and tenants failing to meet their financial obligations may face legal consequences.
Filing an Eviction Lawsuit: Legal Procedures
If a tenant does not address the issues outlined in the eviction notice, the landlord may proceed to file an eviction lawsuit, also known as an unlawful detainer action. This legal procedure involves submitting a complaint to the court, specifying the reasons for eviction and seeking a court order to regain possession of the property.
Court Hearing and Judgment: The Legal Process Unfolds
After filing an eviction lawsuit, both parties are summoned to a court hearing. During the hearing, each party presents their case, and the judge makes a judgment based on the presented evidence and applicable laws. If the court rules in favor of the landlord, a judgment for possession is issued.
Execution of Eviction: Regaining Possession
Following a court judgment, the landlord may obtain a writ of possession, allowing law enforcement to physically remove the tenant from the property. The execution of the eviction involves coordinating with law enforcement to regain possession of the premises. This step is often considered a last resort and is carried out under the supervision of authorities.
Aftermath of Eviction: Tenant’s Responsibilities
Once evicted, tenants face several responsibilities, including removing personal
