Negotiating lease terms
Lease Obligations: Navigating Responsibilities in Business
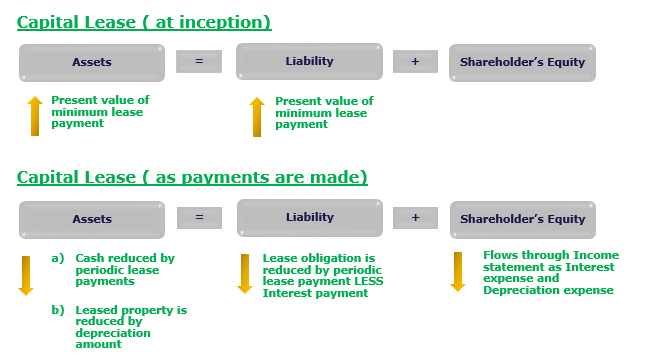
Lease obligations play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of business relationships and financial commitments. As organizations seek to optimize their operational efficiency and resource management, understanding and managing lease obligations become paramount.
Understanding Lease Obligations
Lease obligations encompass the contractual responsibilities that arise when a business enters into a lease agreement for a property, equipment, or other assets. These obligations are legally binding and outline the terms and conditions under which the lessee can use the leased asset. It involves financial commitments, maintenance responsibilities, and adherence to specific terms throughout the lease duration.
Financial Implications of Lease Obligations
One of the primary aspects of lease obligations revolves around financial commitments. Lessees must adhere to payment schedules outlined in the lease agreement. This includes rent, maintenance fees, and any other specified charges. Failing to meet these financial obligations can result in penalties or legal consequences. Proper budgeting and financial planning are essential to fulfill these commitments seamlessly.
Operational Efficiency and Lease Management
Effectively managing lease obligations contributes to operational efficiency. Businesses need to keep track of lease terms, renewal options, and important deadlines to avoid any disruptions in their operations. Utilizing technology, such as lease management software, can streamline the process, ensuring that all lease obligations are met promptly. This proactive approach helps businesses avoid last-minute challenges and uncertainties.
Negotiating Favorable Lease Terms
Negotiating favorable lease terms is a strategic aspect of lease management. Businesses should carefully review and negotiate terms related to rent increases, maintenance responsibilities, and lease duration. Engaging in open communication with landlords or lessors can lead to mutually beneficial agreements that align with the business’s long-term goals.
Legal Compliance and Lease Obligations
Lease agreements often come with legal complexities that businesses must navigate. Understanding and complying with local, state, and federal regulations related to leasing is crucial. This includes zoning laws, environmental regulations, and other legal considerations that may impact the use of the leased property or assets.
Adapting to Changing Business Needs
Business environments are dynamic, and lease obligations should allow for flexibility to adapt to changing needs. Including provisions for subleasing or modifying the lease terms in response to business growth or contraction ensures that the lease remains aligned with the organization’s evolving requirements.
Ensuring Transparency in Lease Communication
Clear communication between the lessor and lessee is vital in lease management. Both parties should maintain transparency regarding any changes, concerns, or issues related to the lease obligations. Regular communication helps build a strong working relationship and minimizes the risk of misunderstandings that could lead to disputes.
In conclusion, lease obligations are a fundamental aspect of business operations, impacting financial stability, operational efficiency, and legal compliance. Effectively managing these obligations requires a proactive approach, strategic negotiation, and adherence to legal regulations. By understanding and addressing lease obligations comprehensively, businesses can create a solid foundation for sustainable growth.
For more insights on lease obligations and effective lease management, visit Lease Obligations.
Navigating Lease Termination Penalties: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding Lease Termination Penalties: A Comprehensive Guide
Lease termination is a complex process, and understanding the associated penalties is crucial for both landlords and tenants. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of lease termination penalties, shedding light on key considerations for a smoother experience.
1. Importance of Reading Lease Agreements Thoroughly
Lease termination penalties are typically outlined in the lease agreement, making it paramount for both landlords and tenants to read the document thoroughly. Understanding the terms and conditions related to termination fees, notice periods, and other penalties is the first step in navigating the process.
2. Common Types of Lease Termination Penalties
Lease termination penalties can take various forms. Common types include early termination fees, loss of security deposits, and potential legal consequences. This section delves into each type, offering insights into when and how these penalties may apply.
3. Early Termination Fees: Calculating the Cost
For tenants considering ending their lease early, early termination fees are a key consideration. This paragraph explores how these fees are typically calculated, providing tenants with a clearer understanding of the financial implications associated with terminating a lease before its natural expiration.
4. Impact on Security Deposits
Security deposits are a standard part of most lease agreements, serving as a financial safeguard for landlords. In cases of lease termination, the impact on security deposits is significant. This section discusses how landlords may use the security deposit to cover unpaid rent or damages and the importance of leaving the property in good condition.
5. Legal Consequences for Breach of Contract
Lease agreements are legally binding contracts, and terminating a lease prematurely may result in legal consequences. This part of the guide explores the potential legal implications for both landlords and tenants, emphasizing the importance of seeking legal advice in complex situations.
6. Notice Periods and Proper Communication
Many lease agreements require a specific notice period for termination. Proper communication between landlords and tenants is crucial during this stage. This paragraph highlights the importance of adhering to notice periods and maintaining open lines of communication to minimize potential conflicts.
7. Negotiating Terms Amicably
In some cases, tenants may find themselves in situations where early termination is necessary. This section discusses the possibility of negotiating terms amicably with landlords. Exploring options such as subleasing or reaching a mutual agreement can help alleviate the impact of termination penalties.
8. Seeking Legal Advice
For both landlords and tenants facing challenges during the lease termination process, seeking legal advice is a prudent step. This paragraph emphasizes the importance of consulting with legal professionals who specialize in real estate law to navigate complex situations and understand rights and responsibilities.
9. Mitigating Financial Impact
Understanding lease termination penalties is not only about recognizing potential costs but also finding ways to mitigate the financial impact. This part of the guide provides practical tips for tenants to minimize penalties and landlords to recover losses through a fair and transparent process.
10. Ensuring a Smooth Transition
In conclusion, navigating lease termination penalties requires
Navigating Rental Expenses: Understanding Costs and Budgeting

Decoding Rental Expenses: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Costs and Budgeting
Renting a property involves more than just the monthly rent payment. From security deposits to utility bills, understanding the various rental costs is crucial for tenants to manage their budget effectively. Let’s delve into the intricate world of rental expenses and how tenants can navigate them wisely.
Breaking Down the Monthly Rent
The monthly rent is the most visible and significant rental expense. It covers the cost of occupying the property and is typically due on a monthly basis. Understanding the terms of the lease agreement, including the amount, due date, and acceptable payment methods, is essential for tenants to stay on top of this primary expense.
Navigating Security Deposits
Security deposits are common in rental agreements, serving as a form of financial protection for landlords. While tenants can often expect to have their security deposit refunded upon the lease’s conclusion, understanding the conditions for retaining or refunding this deposit is crucial. It’s advisable for tenants to conduct a thorough move-in inspection and document the property’s condition to ensure a smooth return of the deposit.
Utility Bills: An Often Overlooked Expense
Utility costs can significantly impact the overall rental budget. These include electricity, water, gas, and sometimes even internet and cable. Understanding which utilities are included in the rent and which are the tenant’s responsibility is vital. Monitoring utility usage and exploring energy-efficient practices can help tenants manage these costs effectively.
Maintenance and Repairs: Unforeseen Expenses
While landlords are typically responsible for major repairs, tenants may be responsible for minor maintenance issues. It’s essential to clarify these responsibilities in the lease agreement. Having a budget set aside for routine maintenance and minor repairs can prevent financial surprises and ensure a well-maintained living environment.
Insurance: Protecting Your Belongings
Rental insurance, although not always mandatory, is a wise investment for tenants. It protects personal belongings in the event of theft, damage, or natural disasters. Understanding the coverage and cost of rental insurance options is crucial for tenants to make informed decisions about their level of protection.
Understanding Late Fees and Penalties
Late fees can quickly escalate rental costs if tenants fail to pay their rent on time. It’s imperative to be aware of the late fee policy outlined in the lease agreement. Planning ahead and ensuring timely rent payments can help tenants avoid unnecessary penalties and additional financial strain.
Parking and Additional Fees
For tenants with vehicles, parking fees can be an additional expense. Some rental properties charge extra for designated parking spaces or require permits. Understanding the parking situation and associated fees is essential for tenants who own cars. Additionally, tenants should be aware of any other potential fees, such as pet fees or amenity charges, outlined in the lease agreement.
Budgeting Strategies for Tenants
With various rental expenses to consider, effective budgeting becomes a crucial skill for tenants. Creating a detailed budget that accounts for rent, utilities, insurance, and other potential costs allows tenants to manage their finances responsibly.
Renewing a Lease: Strategies for Seamless Extension
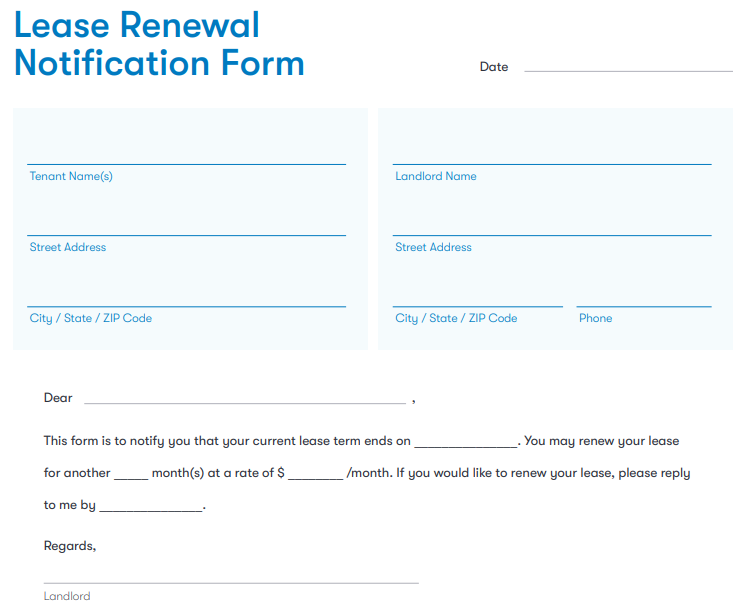
Renewing a Lease: Strategies for Seamless Extension
Lease renewal is a significant milestone in the landlord-tenant relationship, offering an opportunity for continuity and mutual benefit. Whether you’re a tenant looking to extend your stay or a landlord aiming to retain a reliable occupant, the process of renewing a lease requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning.
Assessing the Current Lease Terms
Before initiating the renewal process, both tenants and landlords should thoroughly review the existing lease agreement. Understanding the current terms, including rent amounts, lease duration, and any special conditions, provides a foundation for negotiating and updating the lease for the upcoming term.
Initiating Early Communication
Open and timely communication is key to a successful lease renewal. Landlords should initiate discussions with tenants well before the current lease expires, providing ample time for both parties to express their intentions and negotiate new terms if necessary. Early communication reduces uncertainty and allows for smoother planning.
Renewing a Lease Link: Renewing a lease
Negotiating Updated Terms
Lease renewal is an opportunity to revisit and potentially update the terms of the agreement. This may include adjusting the rent to reflect market changes, modifying lease duration, or incorporating new clauses. Both parties should approach negotiations with flexibility and a willingness to find mutually beneficial terms.
Conducting a Property Assessment
For landlords, the lease renewal process is an opportune time to assess the condition of the property. Conducting a thorough inspection helps identify any necessary repairs or maintenance issues that need addressing before extending the lease. Tenants can also use this time to communicate any concerns or repair requests.
Consideration of Rent Adjustments
Rent adjustments are a common aspect of lease renewals. Landlords may consider market trends, property improvements, or changes in operating costs when determining whether a rent increase is necessary. Tenants, on the other hand, should be prepared to discuss and negotiate such adjustments to reach a fair agreement.
Addressing Tenant Concerns
During lease renewal discussions, landlords should be attentive to any concerns or requests raised by tenants. Whether it’s a desire for specific property improvements, modifications to the lease terms, or addressing maintenance issues, a landlord’s responsiveness can positively influence a tenant’s decision to renew the lease.
Providing Incentives for Renewal
Landlords may consider offering incentives to encourage tenants to renew their leases. This could include a rent discount, upgrades to the property, or other perks. Incentives demonstrate appreciation for reliable tenants and can contribute to a positive and collaborative landlord-tenant relationship.
Renewal Documentation and Signatures
Once both parties have agreed on the renewed lease terms, it’s crucial to document these changes in a written lease renewal agreement. This document should outline the updated terms, including rent amounts, lease duration, and any other negotiated conditions. Signatures from both parties signify mutual agreement and commitment.
Communicating the Renewal Decision
Whether the decision is to renew or not, clear communication is essential. Landlords should promptly inform tenants of their decision, providing any necessary documentation related to the renewed lease. Similarly, tenants should communicate their intentions
